Last updated on November 16th, 2021
You have just started to set aside some savings to invest towards your retirement goals.
However, you are still undecided on how much to allocate to the CPF Investment Scheme (CPFIS) or the Supplementary Retirement Scheme (SRS).
This article will guide you through your dilemma by first making a comparison between the two schemes, followed by some suggestions on how to best save for your retirement using both CPFIS and SRS.
Contents
What is the difference between CPFIS and SRS?
The CPFIS allows Singaporeans to invest their CPF Ordinary Account (OA) or Special Account (SA) funds to improve their returns on their CPF funds. In contrast, the SRS is a standalone scheme which encourages Singaporeans to supplement their retirement funds on top of their CPF using their excess savings.
While both schemes are entirely voluntary, there are certain features which make them stand out from each other.
Comparison between CPFIS and SRS
Let us do a comparison between CPFIS and SRS to find out their similarities and differences.
#1 Contribution Source
To start investing through CPFIS and SRS, you will have to transfer funds over to your CPF Investment Account (CPFIA) and SRS account respectively.
To contribute to your CPFIA, you can transfer funds from either your CPF OA or SA.
Once transferred to your CPFIA, these funds will lose the preferential interest rate enjoyed under their respective accounts.
Here are the interest rates that you can receive for each account:
| CPF Account | Interest Rate |
|---|---|
| OA | 2.5 – 3.5% p.a. |
| SA | 4 – 5% p.a. |
As such, I would recommend that you only invest in products which has the potential of beating these interest rates. Otherwise, it would be better to leave your funds in this almost risk-free accounts!
Meanwhile, you can contribute to your SRS account only through cash or cheque in SGD via the bank that you opened your SRS account in.
#2 Base Interest
If you leave your funds untouched in both your CPFIA and SRS account, they will only generate an interest of 0.05% per annum.
This interest is the same as that of a savings bank account in Singapore.
For funds in your CPFIA, this interest rate is much lower compared to leaving them in your OA and SA.
As the aim of both schemes is to invest your money for greater returns, you are therefore encouraged to invest your CPFIA and SRS funds immediately after you make each contribution.
#3 Investment Restrictions
You can invest your savings in both your OA and SA under CPFIS. However, you can only invest the remainder after setting aside both:
- $20,000 in your OA
- $40,000 in your SA
Furthermore, you are only able to invest a maximum of 35% and 10% of your investible savings in stocks and gold respectively with your CPF OA.
Your investible savings is the sum of your balance in your CPF OA and the amount of CPF withdrawn for your investment and education.
As an example of how to calculate your investible savings, we take the CPF OA profile of a hypothetical person, John:
| OA Balance | $50,000 |
| Amount withdrawn for investment (CPFIS) | $30,000 |
| Amount withdrawn under education (CPF Education Loan Scheme) | $10,000 |
| Amount withdrawn under housing (CPF Housing Scheme) | $100,000 |
| Total investible savings | $90,000 |
With his investible savings of $90,000, here’s how much he can invest in certain products:
| Product | % of Investible Savings | John’s Investible Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Stocks | 35% | $31,500 |
| Gold | 10% | $9,000 |
Amounts withdrawn to pay for your housing is not factored into the calculation of your investible savings.
If you’re worried about having to calculate all of this, fret not! You can bypass these calculations and view your funds available for investment conveniently through the myCPF app, under ‘My Investment’.
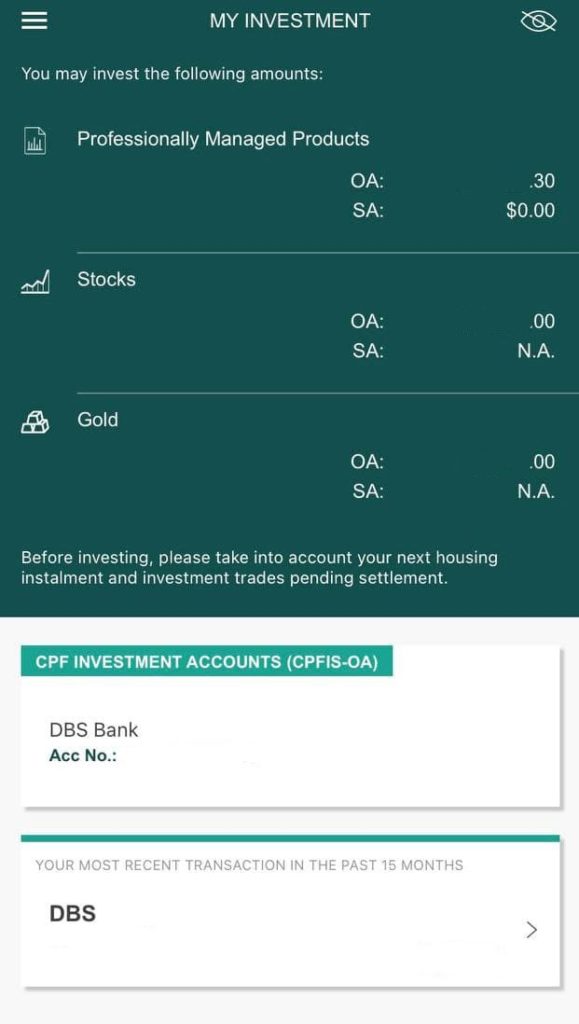
Professionally managed products refer to all investible products under CPFIS, with the exception of stocks and gold.
I personally like this page, as it saves you the hassle of having to calculate your investible amounts manually.
Meanwhile for your SRS, there are no limits on the how much you can invest in the various investment products. However, there is a contribution cap of $15,300 each year if you are a Singapore citizen.
#4 Investment Products
The following are some of the investment products you can invest using your CPFIA and SRS account:
| Investment Product | CPF OA | CPF SA | SRS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Trusts | Yes | Yes (Higher risk products not included) | Yes |
| Investment-linked Insurance Plans (ILPs) | Yes | Yes (Higher risk products not included) | Yes |
| Stocks | Yes (Up to 35% of investible savings) | No | Yes |
| ETFs | Yes | No (No products available) | Yes |
| Annuities | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Endowment Policies | Yes | Yes | Yes (Single premium endowment plans only) |
| Gold | Yes (Up to 10% of investible savings) | No | Yes |
| Singapore Government Bonds | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Treasury Bills | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Your CPF OA and SRS allows you to invest in a wide range of investments
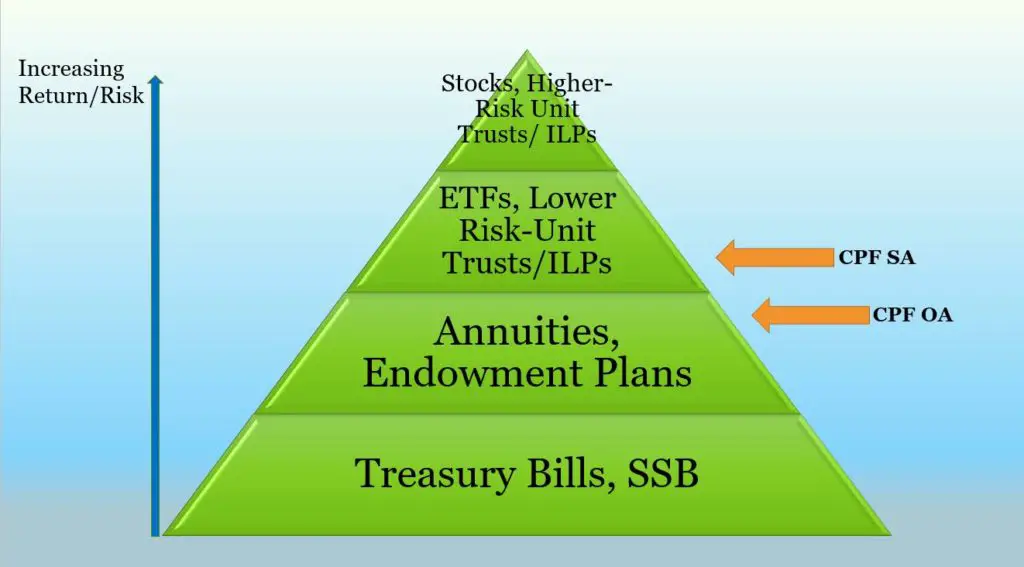
You can use your CPF OA and SRS monies to invest in investments ranging from low risk Singapore Government Bonds and Treasury Bills to the highest risk (and potentially high yielding) Unit Trusts and stocks.
The following infographic shows the potential returns (and risk) you can expect by investing in the various investment products in the long run. The returns of the CPF OA and SA have also been included as references.
With the larger variety of investment products available, you have the opportunity to customise your personal retirement portfolio, which I strongly advocate as everyone has different retirement goals.
Factors to consider when customising your retirement portfolio include your:
- Time horizon
- Risk level
- Target retirement budget
One popular way of calculating how much you need to save for your retirement is the 25x rule. By estimating your total retirement savings as 25 times your annual retirement budget, it gives an easy way for you to arrive at a figure you should save for your retirement.
Your CPF SA only allows investment in a narrower range of safe investments
Meanwhile, the funds in your CPF SA are meant solely for your retirement. These funds will form a significant portion of your post-retirement payouts under CPF Life.
To minimise the chances of losing a large amount of your CPF SA funds during bearish years, products which are approved for CPF SA investments tend to fall into lower risk categories.
By only allowing investments in products with lower risk, the chances that you’ll have inadequate savings for your retirement is reduced.
#5 Charges by your agent bank
Here are some of the charges that you’ll incur when investing using these schemes:
CPFIA
Apart from commissions made to your brokerages and fund management companies, you will also need to pay charges to your agent bank to process your CPFIS investments.
This fees come in two kinds:
- One-off transaction charge when you buy/sell an investment
- Periodic service charges every quarter
The following table displays the charges for
- Stocks
- Unit Trusts
- ETFs
which are bought directly from your agent bank:
| Bank | Transaction Charge | Service Charge |
|---|---|---|
| DBS | $2.50 per 1,000 shares (Max. $25) | $2 per counter per quarter* |
| OCBC | $2.50 per 1,000 shares (Max. $25) | $2 per counter per quarter |
| UOB | $2 per 1,000 shares (Max. $20) | $2 per counter per quarter |
However, if you make your investments for:
- Endowment Plans
- ILPs
- Authorised brokerages (eg FSMOne, POEMS)
- Roboadvisors (eg Endowus, Syfe)
- Fixed deposits
your transaction and service charges are fixed at $2 – $2.50 and $2 per quarter respectively.
| Bank | Transaction Charge | Service Charge |
|---|---|---|
| DBS | $2.50 | $2 per quarter |
| OCBC | $2.50 | $2 per quarter |
| UOB | $2 | $2 per quarter |
The transaction and service charges are mostly the same across all the banks. The only exception is UOB offering a slightly lower transaction charge.
The transaction charges discourage the use of regular savings plans in small amounts. By making many small transactions over time, a large portion of your savings will be eaten by the accumulated charges!
SRS
On the other hand, agent bank charges have been waived for most investments in your SRS account.
The only exception is for Singapore Savings Bonds (SSBs). You will need to pay a $2 transaction fee for application and redemption requests.
#6 Incentives
There are no direct incentives for topping up your CPFIA from your OA or SA.
You may want to note that topping up your CPFIA is different from the Retirement Sum Topping-Up Scheme. The RTSU gives you tax incentives for topping up your SA/RA.
In contrast, topping up your SRS account will qualify you for tax relief equal to the contributions you made that year. Therefore, the amount of tax relief you will receive is based on the annual income bracket you fall under.
#7 Withdrawal of Investments
As the purpose of CPFIS and SRS are for our retirement expenses, it is important to know when we can start withdrawing our monies from both schemes so we can better plan our retirement age.
CPFIA
After setting aside your Full Retirement Sum (FRS) in your CPF Retirement Account (RA) at age 55, you can withdraw the balance your CPFIA in cash anytime.
Gradually withdrawing your CPFIA funds helps to both manage your spending and grow your remaining savings.
Alternatively, you can use your CPFIA funds to top up your RA anytime before your CPF LIFE payout begins (at age 65 – 70) to accumulate your FRS. Through CPF LIFE, you are able to receive monthly payouts for life.
If you desire larger payouts from CPF LIFE, you may even top up your RA all the way to the Enhanced Retirement Sum (ERS), the maximum permissible amount allowed.
The ERS is 1.5 times the amount of the FRS.
SRS
While you can withdraw your SRS funds anytime, it is recommended that you do so after your statutory retirement age.
Withdrawing before the statutory retirement age will result in a 5% penalty of the amount withdrawn, and a full reversal in tax benefits.
From the year that you make your first penalty-free withdrawal, you will be given up to 10 years to withdraw all your SRS funds. Furthermore, 50% of the withdrawal amount will be subjected to income tax for that year.
A penalty-free withdrawal refers to a withdrawal made at or after the statutory retirement age.
Any balance in your SRS account at the end of the 10 year period will be ‘deemed withdrawn’, a process which subjects 50% of the remaining balance to a one time taxation. You may still retain the balance thereafter; however, it will be regarded as a normal investment in future.
Verdict
Here is a summary of the comparison between the CPFIS and SRS:
| CPFIS | SRS | |
|---|---|---|
| Contribution Source | From CPF OA or SA | Cash or cheque |
| Base Interest | 0.05 % p.a. | 0.05 % p.a. |
| Investment Restrictions | – Set aside $20,000 in OA and $40,000 in SA first – OA funds only: Max. 35% and 10% of investible savings in stocks and gold respectively | Contribution cap of $15,300 p.a. |
| Investment Products | – OA funds: Wide range of investments – SA funds: Narrower range of ‘safer’ investments | Wide range of investments |
| Charges by your agent bank | – One-off transaction charge – Periodic service charges | Wavied (except for SSBs) |
| Incentives | No direct incentives | Tax reliefs |
| Withdrawal of investments | Withdrawal from age 55 once FRS set aside in RA | – Can withdraw anytime (Subject to penalty and reversal of tax reliefs before retirement age) – 50% of penalty-free withdrawals are taxable – Up to 10 years to withdraw SRS funds from first penalty-free withdrawal |
How can I make use of my CPFIA and SRS for my retirement?
Although it may sound intimidating at first, it is possible to make use of both your CPFIA and SRS for that well rounded retirement plan.
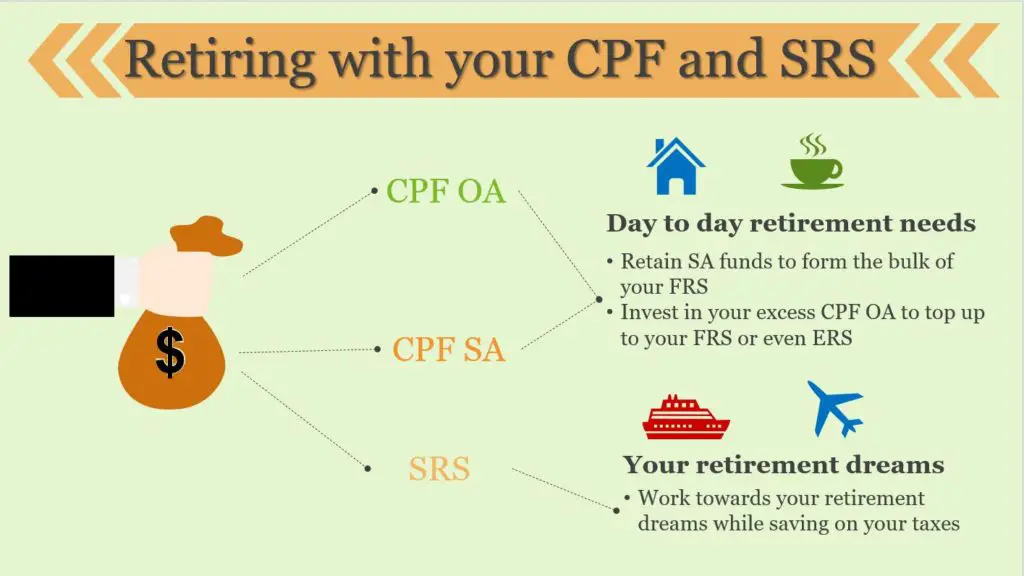
Here is one possible strategy to allocate your CPFIA and SRS funds for your retirement:
Invest using your CPF OA for your day to day needs
While the CPF OA is a safe haven to save up for your retirement with its stable interest rate, its 2.5% – 3.5% interest per annum leaves more to be desired when investing for long term goals such as your retirement.
You may want to invest only your excess OA monies after setting aside your spending needs such as housing.
For example, we take the example of investing our OA funds in the S&P 500 through the LionGlobal Infinity US 500 Stock Index Fund, which tracks the S&P 500’s performance through the Vanguard® U.S. 500 Stock Index Fund.
You can invest in the LionGlobal Infinity US 500 Fund through Endowus.
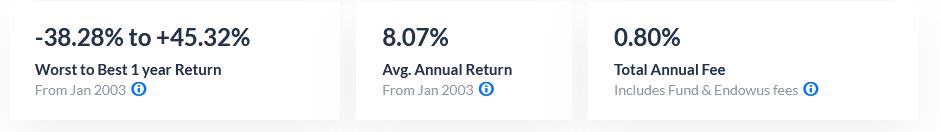
After accounting for fees, this fund has yielded an average of about 7.2% per annum over the past 18 years. Using the power of compound interest, an investment in this fund would have returned much more than leaving them in your OA!
Although this figure does not conclusively predict the future returns of this fund, we can still conclude that investing your OA funds gives you a very good chance of beating the OA interest rates in the long term.
With your increased returns, you get a strong advantage to top up your RA from age 55 to save up to your FRS or even your ERS.
After covering your retirement sum, sit back and relax as you receive your lifelong payouts under CPF LIFE once you hit the payout eligibility age of 65 years old.
Invest using your SRS for your retirement dreams
Given that your SRS has a 10 year withdrawal period starting from your first penalty-free withdrawal, your SRS funds are not meant to fully support your retirement needs.
With the current life expectancy of Singaporeans in 2020 at 84 and expected to rise further, our SRS can only last through a part of our retirement period.
However, since your day to day retirement needs have been covered by your CPF, you can now make your retirement dreams come true with your SRS funds!
Be it that round the world holiday or the new hobby that you want to pick up, you can rely on our SRS investments to make all of them happen.
You can find out more about maximising your SRS with this guide.
Keep your CPF SA funds in your SA account to accumulate interest
Now that your SRS and excess OA funds are fully invested, we will need a stable foundation to ensure that your savings will not be adversely affected by a sudden financial downturn near your retirement.
The role of this foundation can be borne by your SA funds. By leaving them in your SA, your monies enjoy a decent 4 – 5 % interest rate that is essentially risk free.
It is almost impossible to find products in the market which offer such high guaranteed returns combined with such a low risk.
Therefore, there is not much point in investing your SA funds. Instead, they are better off left in your SA to form the bulk of your FRS in your RA.
One method that emphasises accumulating in your CPF SA that is gaining traction among Singaporeans is the 1M65 movement pioneered by Loo Cheng Chuan.

Using some math and the power of compound interest, Loo proposes that if you and your spouse each save $130,000 in your CPF SA and MA at age 30, both of you will have a combined CPF balance of $1 million at age 65!
As $130,000 in your SA savings is definitely unattainable from your salary alone, you will need to perform top ups to reach this amount.
However, from my personal opinion, I prefer investing my excess savings instead of topping up my SA. This is because I can use the long time horizon to achieve greater returns.
The info graphic below summarises the entire plan on how you can retire with your CPF and SRS.
Can I transfer funds from my CPF to my SRS account?
Even though both your CPF and SRS have a similar goal of providing for your retirement, you are unable to transfer funds from your CPF to your SRS account. This is because the CPF and SRS belong to different schemes.
Due to the strict restrictions in withdrawing your CPF monies, you are unable to withdraw them under most conditions.
The only other purposes that you can withdraw your CPF OA are for your housing and further education. And even then, you will need to repay the borrowed amount back to your OA.
As such, it is important for you to budget your investment spending in both accounts wisely first before you start contributing to them!
Conclusion
While you can use both your CPFIS and SRS to invest towards your retirement, both of them belong to two different schemes. Your funding allocation to each scheme is important, as top ups to them are usually irreversible or come with penalties.
By understanding their differences, we can create a well rounded retirement plan using our CPF and SRS which encompasses both our day to day needs and our retirement goals.

Do you like the content on this blog?
To receive the latest updates, you can follow us on our Telegram channels (Personal Finance or Crypto) and Facebook.
Are you passionate about personal finance and want to earn some flexible income?