Today, blockchain has quite a few problems to solve. It has high transaction fees and slow processing speeds. Moreover, the chains do not communicate with each other.
Data on the blockchain differs from the data on the Internet that we know.
Polygon and Chainlink are top blockchain platforms that solve these issues. This makes them valuable as companies.
However, how do they differ? Let’s explore their differences in this article!
Contents
- 1 The difference between MATIC and LINK
- 2 Main Network Functions
- 3 Polygon network uses Plasma Chains
- 4 Chainlink is an oracle network
- 5 Main Coin Functions
- 6 Earning Money Through the Network
- 7 Earning Through Staking Coins on Platforms
- 8 Most Anticipated Projects
- 9 Companies behind MATIC and LINK
- 10 Final Verdict
- 11 Conclusion
The difference between MATIC and LINK
Polygon uses Plasma to scale the Ethereum network while Chainlink is an oracle that links off-chain data to the blockchain. Polygon is building the ultimate decentralised Ethereum scaling platform while Chainlink is focused on developing a tamper-proof “blockchain middleware” for almost all blockchains. They are non-exclusive networks as Chainlink is also used in numerous Polygon apps.
Main Network Functions
How does the network function? Let’s explore the technical aspect of the two blockchain networks:
Polygon network uses Plasma Chains
Polygon is a Layer 2 chain that scales Ethereum, which is a Layer 1 chain.
Layer 2 is built upon Layer 1, without changing the underlying layer. Layer 2 (Polygon) helps Layer 1 (Ethereum) to scale better while enjoying the security that Layer 1 offers.
The most common problems of Ethereum blockchain are:
- High transaction costs (also known as gas fees)
- Slow processing speed
- Poor user experience
Polygon was created to solve these problems, as described in their original white paper. At the same time, the network can make use of Ethereum’s existing ecosystem and decentralised features.
How the Polygon network works
The key to Polygon’s network is its Plasma framework, which uses plasma bridges.
Plasma bridges help to move assets between the main chain and side chains. Root chains (or main chains) can be seen as Layer 1 while sidechains are Layer 2.
Photo by sergio souza from Pexels
Like expressways on the roads, Polygon provides a faster and alternative path than normal paths. If the Ethereum network is congested like a traffic jam, a user move their asset from Ethereum to the Polygon child chains (or sidechains) and transact there instead.
To transfer an asset such as a non-fungible token (NFT), the process takes place with the following steps:
- Transfer assets from the main chain to side chain
- Lock assets on the main chain
- Duplicate assets on the side chain
- Transfer within the side chain
- “Destroy” assets on the side chain
- Unlock assets on the main chain
Essentially, this is what the Plasma framework is about. It frees up the base network by diverting the transactions to the side chains.
Chainlink is an oracle network
Different from Polygon, Chainlink operates as an oracle network. It is a vital part of blockchains.
An oracle is a blockchain middleware that creates a secure connection between smart contracts and various off-chain resources that they need to function.
Definition of a blockchain oracle by Chainlink
Even though blockchain applications have many functions, they may still need certain data that is outside of the blockchain system.
This is also known as off-chain data.
For example, the Uber app needs Google Maps to track the location of the car and guide the driver to the destination within the app.
This location tracking from Google is a set of data from outside of the Uber app.
Usually, this process of connecting data is simple since they operate on the same computing system.
They record data and transmit data in the same way, which makes them compatible to connect data across the platforms.
However, if Uber was on the blockchain, there is a problem translating the Google Maps data into data that the blockchain can understand.
In this way, Chainlink can help to connect the external data (in this case, Google Maps) and apps on the blockchain (our blockchain Uber).
So, what’s the difference?
The two networks have different priorities. Polygon is specific to scaling the Ethereum network, while Chainlink focuses on bridging the off-chain data to the on-chain data. Either way, both are important to the blockchain ecosystem.
In fact, the two networks are in collaboration as well. Chainlink Keepers launched on the Polygon network and decentralised applications (dApps) on Polygon often use Chainlink as an oracle.
Main Coin Functions
There is a difference between the network and coin. Usually, coins are the currency that facilitates transactions on the network.
Let’s explore the functions of the two coins:
Polygon (MATIC) coins allow you to pay fees, validate and delegate.
While the network is called Polygon, the coin is known as MATIC.
Polygon is to Matic as Ethereum is to ETH.
CoinDesk
MATIC coins are extremely successful among retail traders, with an astronomical 29100% increase in a year. Compared to the general crypto market, the gain in MATIC is impressive.
What is the role of the MATIC token?
It is a method of payment on the Polygon network. To perform tasks like creating an asset on the sidechains, the users have to pay transaction fees, which are in MATIC coins.
Another role of the tokens is to secure the network in its Proof-of-Stake mechanism.
There are validators and delegators in the network. Validators run nodes and secure the network. Delegators, on the other hand, assign their coins to a validator for rewards.
Validators will have an option to charge a commission on the reward earned by delegators.
If they violate the rules of the network, they will be punished and their coins will be forfeited. This is commonly called slashing.
Validators and delegators secure the network by staking their MATIC in the staking contracts, which are used to achieve consensus and ensure the security of the network.
Roles of validators and delegators, according to Polygon
How much do these validators and delegators earn? We will discuss this in the following section.
ChainLink (LINK) – Pay for transactions
If you run a blockchain app that needs Chainlink as a middleman, you will have to use LINK tokens to pay for the transaction fees.
For example, Google uses Chainlink to build applications across the blockchain and cloud on Ethereum and Google Cloud.
Source: Google Cloud
Chainlink is perfect for such hybrid applications. To pay for the transactions on the application, Google has to pay fees in LINK.
As a retail investor, there are limited uses of the coin. This is because Chainlink is mainly for businesses to perform transactions, rather than people like you and me.
Instead, you can invest in the value of the coin by trading and holding. If more people adopt Chainlink to make payments, the value of the token may start to increase!
Another way is to operate a node to earn these transaction fees paid by these businesses.
Perhaps you heard of mining cryptocurrencies, but you cannot mine Chainlink tokens. However, you can operate a node to collect transaction fees, which are paid in LINK tokens.
Earning Money Through the Network
We discussed coin functions, but what about the ways to earn the coin?
If you are looking for higher returns while willing to take higher risks, you can also earn money through the Polygon and Chainlink networks.
These two networks have different methods for investors, like yourself, to stake on the network directly.
Let’s explore the options in the section!
Polygon – Stake on Network
We briefly mentioned coin functions in the previous section. However, how much does a validator or validator earn?
The average earnings are 4.5% – 5% per year for being a delegate or validator.
The exact percentage you earn will depend on several factors. These factors could give you a higher reward:
- A high number of people staking Polygon
- Coins that have been in the wallet for a long time
- A high number of blocks generated by the wallet
- Lower transaction fees
The best-case scenario is that you earn 8% per year, but this will only happen if the network volume and transaction fees are low. You can expect to earn between 2% and 4% per year in most cases.
The Tech Trend
For a detailed guide on how to stake on the Polygon network, here is a full guide on how to through Metamask.
Chainlink – Operating a node
Another way to earn crypto is to run a node. You can do this on Chainlink.
You do not need extensive hardware to run a node.
However, you will need to download the necessary software on your computer, and ensure that you have enough storage and processing speed to run the node efficiently.
Here are some technical requirements to run a Chainlink node:
- Download Docker-CE
- The computer should run on at least 1 core and 1 GB of RAM
- You will need to have a connection to an Ethereum client. The different types of clients can be found here.
Setting up a node is extremely technical, and it requires much more effort compared to being a liquidity provider on Uniswap. However, the rewards for operating a node are much higher!
Source: Market.link
The daily revenue of running a node can be up to $2000 USD per day! These returns are much higher than providing liquidity on Uniswap.
If you would like to read more about it, here’s a guide by Chainlink to help you set up your first node.
Earning Through Staking Coins on Platforms
A great way to earn passive income is to stake coins on platforms and receive interest. It is also easy to set up and beginner-friendly, compared to participating in nodes and validation.
Let’s compare the interest rates across the different platforms:
Staking MATIC on platforms
| Platforms | Interest Rate (per year) |
|---|---|
| Binance | 11.34%, MATIC locked for 30 days 12.2%, 60 days 14.09%, 90 days |
| Crypto.com | 6.0%– 14.0%, depending on the staked amount and staked duration |
| Gemini | 2.02% |
| BitFinex | Up to 41% |
The most straightforward option to stake MATIC is on Gemini. It offers a yearly interest rate of 2.02% without complex conditions.
For Crypto.com, the range of interest rates is around 6% to 14.0%. You can get the highest interest rate by staking 4,000 Crypto.com coins (CRO) on their platform for 3 months.
As for staking on Binance, the minimum locked amount is 1 MATIC and there are limited slots for staking MATIC. The stake may be sold out, like in the screenshot below.
Source: Binance
On MATIC’s latest collaboration with BitFinex, the staking rewards for MATIC is up to 41% annually.
Bitfinex has received 90 million MATIC from Polygon to sponsor enhanced staking rewards for Bitfinex users.
BitFinex’s Press Release
There is no minimum staking amount, however, there is a minimum staking reward of about US$0.50. More information can be found on BitFinex’s website.
Staking LINK on platforms
| Platforms | Interest Rate (per year) |
|---|---|
| Binance | 1.4%, flexible stake duration |
| Crypto.com | 0.5% – 5.0%, depending on staked CRO and fixed stake duration |
| Gemini | 1.35% |
| BitFinex | Not available |
The highest interest rate return on Chainlink is 5% per year on Crypto.com, with a 4,000 CRO stake for 3 months.
If you would prefer a straightforward option, Gemini is also the easier option with a 1.35% return per year.
The rates on Binance change often, so do check their website for the latest rates. Usually, they offer stake flexible stake, 1 month and 3 months stake. Currently, they offer 1.4% per year for no fixed stake duration.
Most Anticipated Projects
For long term investments, it is crucial to know the roadmap for the coin and network.
Here are key future developments for both coins:
Wide adoption of Polygon
In an interview, Polygon’s co-founder, Jaynti Kanani, revealed that Polygon is used by the government of Maharashtra (the second-most populous state in India). Results of COVID tests can be verified through Polygon.
So many people are using Polygon, but maybe they don’t know it.
Jaynti Kanani, Polygon’s co-founder
The network has a wide adoption. Thanks to the network effect of Ethereum, Polygon has a wide reach. Thus, it has a huge potential to work on various projects and grow in the long term.
In 2022, Polygon enabled users to burn their tokens. This means destroying their coins and reducing the supply of circulating MATIC in the ecosystem.
Why would they do this?
This process, known as EIP-1559, makes the coins deflationary.
“Deflationary pressure causes the base fee to increase automatically if the block is full, the changes will result in fewer spam transactions and lead to less network congestion,”
Polygon team
This highly-anticipated move benefits both validators and delegators.
Source: Polygon Burn
Additionally, Polygon has been ramping up its efforts to scale bigger, through mergers and acquisitions. The company recently merged with the Hermez network and acquired ZK-rollup, to scale the Ethereum blockchain.
Chainlink – Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP)
The most exciting development on DOT is developing a common protocol for smart contract development.
They are creating an open-source standard for cross-chain communication, called the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP).
Here are some reasons why we need this protocol:
- Quickly promote the innovation of application developers on the blockchain.
- Able to combine the abilities of different blockchains and unique assets into one application
CCIP aims to establish a universal connection between hundreds of blockchain networks, both private and public, unlocking isolated tokens and empowering cross-chain applications for all on-chain ecosystems.
Chainlink introduced their latest project, CCIP
Essentially, they want to build the internet of blockchain by having a common language for all blockchains to communicate.
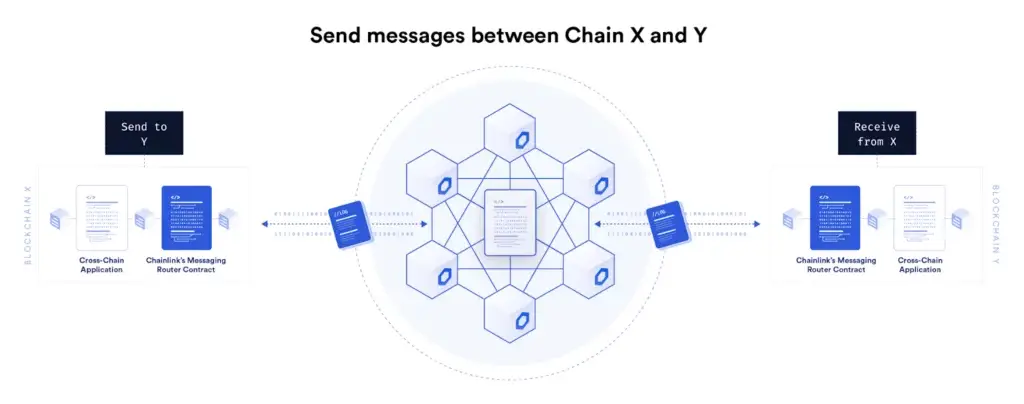
Source: Chainlink
This sets a standard for blockchains and increases the interconnectivity and productivity of the networks.
So, what’s the difference?
Polygon is expanding its core service, which is to scale the Ethereum blockchain. On the contrary, Chainlink is developing a complementary service, which is not their main function as an oracle.
Regardless, both companies are building their ecosystems to make it easier for developers. Polygon provides more tools to scale while Chainlink lays the foundation for different chains to communicate and scale.
Companies behind MATIC and LINK
To look at the value of a cryptocurrency, it is important to consider its management team, who are in charge of the development of the coins. This can help us understand their background and long-term goals for the company, network and coins.
Let’s look at the leaders behind these coins:
MATIC management team
Matic network is based in India and was founded in October 2017.
Its founders are India’s first crypto billionaires, namely Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal and Anurag Arjun. They were joined by Mihailo Bjelic.

Source: CoinDesk
Polygon was rebranded from the Matic Network in February 2021. This is why the coin kept its name MATIC, while the company has been rebranded to Polygon.
The most notable partnerships with Polygon includes Decentraland, Chainlink and MakerDAO, which are relatively big projects in blockchain.
Polygon’s latest high-profile investor is Mark Cuban, who is a billionaire owner of an NBA team. You may have heard of him as an investor on the TV show, Shark Tank. He was a frequent user of the Polygon network before being an investor.
These factors make Polygon more credible as a company to invest in.
Founders of Chainlink
Chainlink was set up in 2017, with Sergey Nazarov as its CEO and Steve Ellis as its CTO. 30% of the coins were allocated to the team members and founders.
Source: icodrops
The parent company of Chainlink is Smart Contract, and the founders have been involved in the space since 2014. They are considered one of the early movers in the blockchain scene.
Many other team members from Smart Contract also moved to Chainlink. With their experience, they can better help develop Chainlink in the long run.
Adding to Chianlink’s credibility, former Google CEO, Eric Schmidt, joined Chainlink Labs as their strategic advisor.
With a strong and experienced team, Chainlink has a strong foundation to build better infrastructure and more value for its users.
Final Verdict
| Chainlink (LINK) | Polygon (MATIC) | |
|---|---|---|
| Network | Oracle | Plasma/Sidechains |
| Purpose | Connects on-chain and off-chain data | Improving the scalability of Ethereum based applications |
| Year of Establishment | 2017 | 2017 |
| Coin Function | Pay for transaction fees on the blockchain | Pay, delegate, validate |
| Best interest rate for staking | 5.0% on Crypto.com, with staked CRO and a fixed duration | Up to 41% on BitFnex (for a limited promotion period) |
| Earning through the network | Operating a node | Staking directly on Polygon through delegation or validation |
| Future Plans | Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) | Wide adoption, deflationary pressures by burning tokens |
| Background of founders | Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis, Founders of Smart Contract | Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal and Anurag Arjun. They were joined by Mihailo Bjelic. |
So which of the two is more suitable for you?
Choose Chainlink if you are integrating blockchain into your business or more technically inclined
Essentially, Chainlink is a business-to-business (B2B) solution on the blockchain. Since most apps still need to draw information from an off-chain source, Chainlink has a strong value in the blockchain ecosystem.
However, it may be overwhelming for a beginner to get started on the Chainlink network directly. Experience is needed to set up a node. Since it is a network adapted for businesses, it is more difficult for a consumer to understand and relate to.
Choose Polygon if you have transactions or develop dApps on Ethereum
As long as your assets are in the Ethereum network, you can benefit from the convenience and speed of the Polygon network.
Regardless of its success in the retail sector, the Polygon network is mainly aimed at improving the experience of developers. If you are a developer on Ethereum, Polygon is extremely useful to create decentralised apps (dApps) that are faster and cheaper than on the main Ethereum network.
However, if your assets or your products are not in the Ethereum network, you will not be able to make use of the Polygon network. Polygon currently does not support dApps that are not on the Ethereum network. It also has no plans of expanding outside of Ethereum.
Conclusion
Both of these networks solve problems on the blockchain. Polygon solves the scalability of the Ethereum network, while Chainlink solves the linking of information on and off the blockchain.
This gives both coins an edge as they have a solid use case on the blockchain behind their tokens.
Polygon and Chainlink are promising projects that are interconnected. They are worth keeping track of in the years to come!

Do you like the content on this blog?
To receive the latest updates, you can follow us on our Telegram channels (Personal Finance or Crypto) and Facebook.
Are you passionate about personal finance and want to earn some flexible income?





